Endoscopic approach of suprasellar arachnoid cyst
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v2i2(May-August).32Keywords:
supra selar, arachnoid cyst, neuroendoscopy, pediatric neurosurgeryAbstract
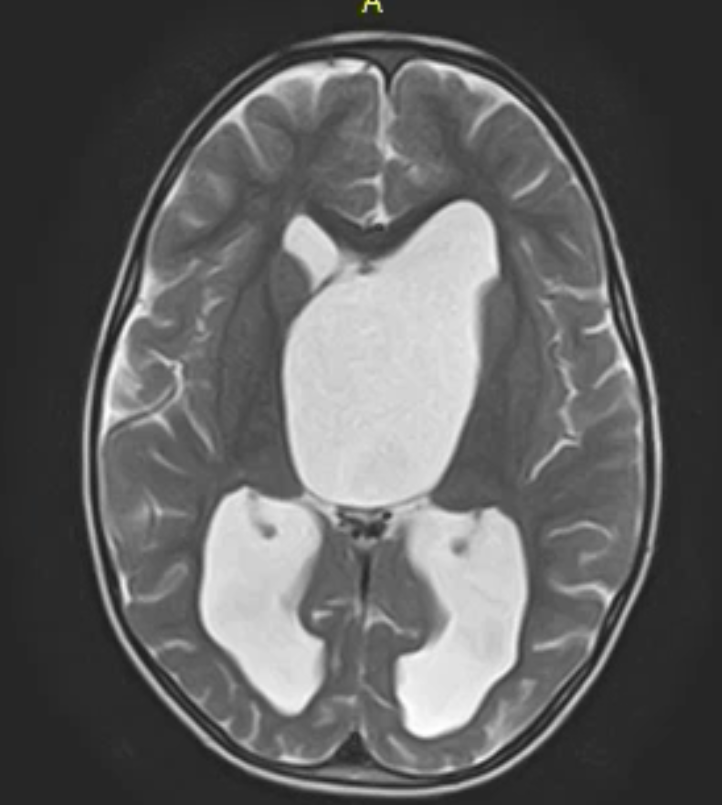
A male 3-year-old child was referred to our service due to increasing head size and mild headache. On physical examination, head circumference was 55 cm (bigger than 97th percentile), the child was conscious, alert and oriented to person, place, time and event, his pupils were isochoric, the light reflex was bilaterally positive, eye movements showed a slight palsy on the abduction of the left eye, and a partial vision loss on the left eye was detected. Gait was also impaired. MRI presented a cystic lesion in the suprasellar region suggesting arachnoid cyst, associated with hydrocephalus. An endoscopic ventricular approach was performed through a straight incision over Kocher’s point. The cyst was easily identified, coagulated with cautery and incised with endoscopic scissors. A ball-valve mechanism was well visualized. Prepontine cistern was also sharply opened and the whole cyst wall was coagulated. The patient was discharged on the second postoperative day showing a clinical improvement. Late head CT presented also a radiologic improvement.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Leo Gordiano Matias, Fernando Luís Maeda, Humberto Belem de Aquino, Enrico Ghizoni

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























