Posterior fossa tumor resection in children: a case report and the role of intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v5i3.220Keywords:
posterior fossa tumors, children, medulloblastoma, intraoperative neuromonitoringAbstract
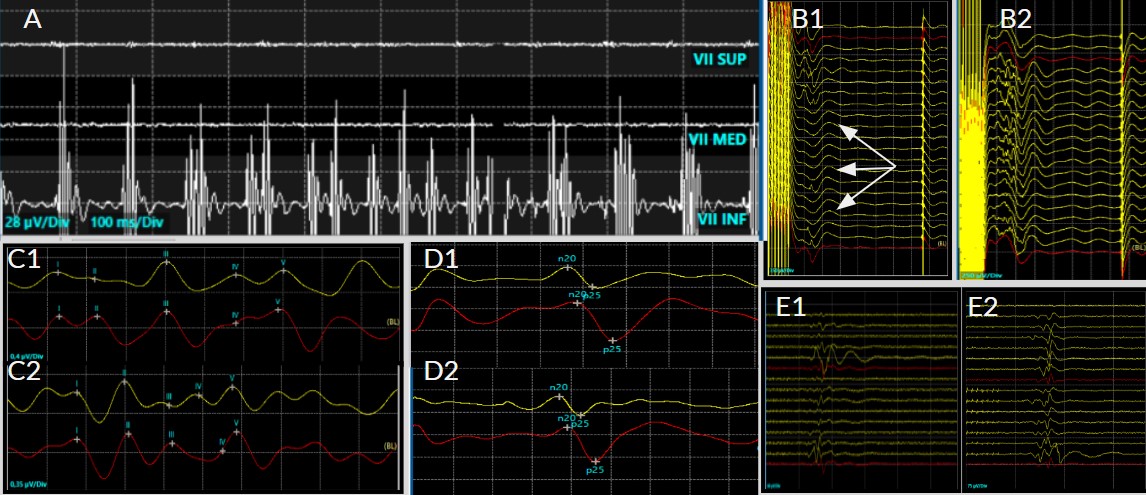
Introduction/Background: Surgery plays a crucial role in the surgical management of posterior fossa tumors in children, but maximizing the resection while preserving function remains challenging. Along with other tools available to the surgeon, intraoperative neuromonitoring aims at improving safety during these complex interventions. This case report highlights the role of real-time intraoperative neuromonitoring during surgery and its impact on the surgeon's decision-making process.
Case report: We present the case of a 10-year-old boy with a fourth ventricle medulloblastoma, who underwent microneurosurgical resection under intraoperative neuromonitoring. The use of neurophysiological monitoring yielded relevant information during the tumor dissection of the floor of the fourth ventricle, the most crucial step of surgery, thus helping the surgeon to change tactics to minimize long-term neurological deficits.
Conclusion: In combination with meticulous microneurosurgery techniques, modern anesthetic regimens, and ultrasonic aspiration, intraoperative neuromonitoring adds up to the surgeon's armamentarium for increasing safety and improving outcomes following surgery for pediatric patients bearing posterior fossa tumors.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Charles Kondageski, Humberto Kluge Schroeder, Antonio Cesar de Melo Mussi, Cezar Massaru Guiotoku, Marcela de Moraes Barros Sousa, Jean Costa Nunes

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























