Posterior fossa hemangioblastoma in children: literature review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v5i3.216Keywords:
neoplasm, tumor, posterior fossa, hemangioblastomaAbstract
Introduction: Posterior fossa hemangioblastomas (HBs) are uncommon benign neoplasms, comprising 1.5-2.5% of intracranial tumors and 7-8% of posterior cranial fossa tumors. They predominantly impact the central nervous system, often localizing within the cerebellar hemispheres of individuals aged 50-60 years, with higher prevalence among adults and limited occurrence in the pediatric population. This review sheds light on the distinctive clinical characteristics of pediatric HBs
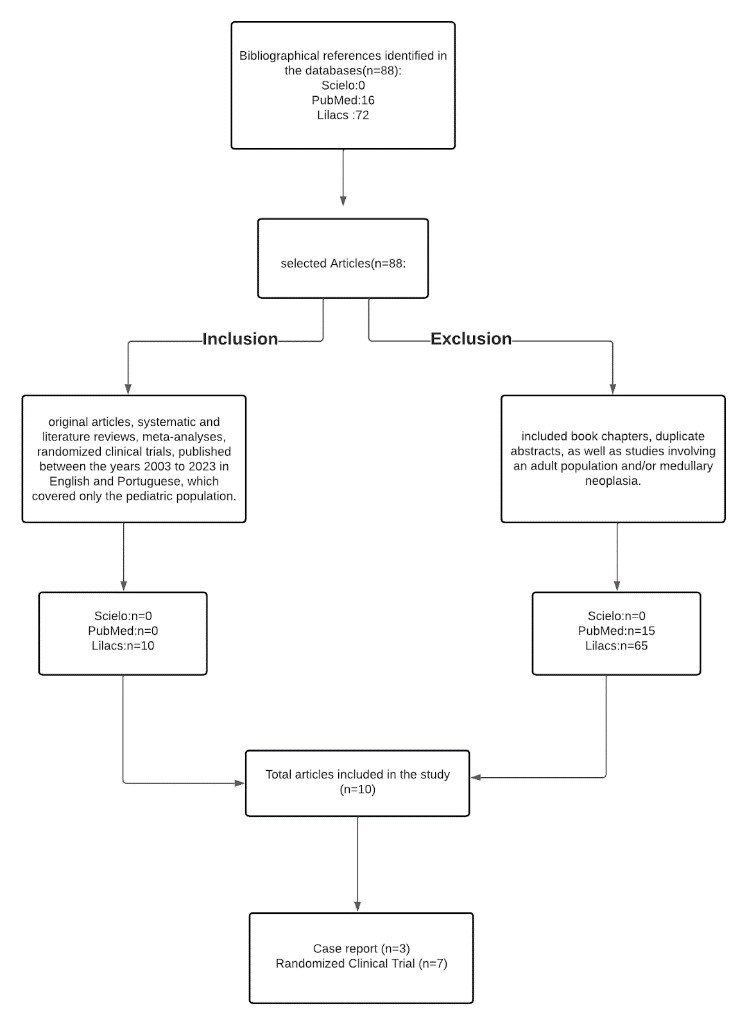
Methods: Employing the PRISMA guidelines, databases like SciELO, Lilacs, and PubMed were meticulously searched, deploying keywords "hemangioblastoma" and "posterior fossa." Inclusion criteria spanned articles published from 2003-2023 in English or Portuguese, focusing on pediatric cases.
Results: The search yielded 16 relevant articles from PubMed and 72 from Lilacs, with SciELO yielding no relevant results. Rigorous assessment against the predetermined criteria identified 10 pertinent articles from Lilacs discussing pediatric posterior fossa HBs, encompassing topics like imaging, pathophysiology, immunohistochemistry, and therapeutic modalities. Diverse themes were explored, including pregnancy-related manifestations, tumor growth patterns, and treatment approaches such as surgical resection, radiotherapy, neuronavigation, and presurgical embolization. Advanced imaging techniques, like high-resolution 3D multifusion medical imaging, were also explored.
Conclusion: Early diagnosis and a comprehensive multidisciplinary strategy are essential in managing pediatric posterior fossa HBs. Genetic insights and advanced imaging techniques, coupled with precise surgical interventions, play a pivotal role in improving prognosis and elevating the quality of life for patients. The genetic context of VHL mutations, the centrality of MRI in early detection, and the prominence of complete surgical resection underscore the multifaceted comprehension indispensable for effective management.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Aline Rabelo Rodrigues, Pedro Lucas Bessa dos Reis, Gabriel Bagarolo Petronilho , Caio Araujo de Souza, Pamela Lopes Carvalho, Ricardo Santos de Oliveira, Rodrigo Inácio Pongeluppi, Matheus Ballestero

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























